Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide
- 3.1 What is a Partition Index?
- 3.2 The Importance of the Partition Index
- 3.3 The Structure of the Partition Index
- 3.4 Understanding the Partition Index in Windows 10
- 3.5 Maintaining the Partition Index
- 3.6 FAQs about the Windows 10 Partition Index
- 3.7 Conclusion
- 4 Closure
Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide
The Windows 10 operating system, like its predecessors, relies on a complex architecture to manage data and ensure smooth functioning. One key component of this architecture is the partition index, a vital element that plays a crucial role in how the operating system interacts with your hard drive. This guide delves into the intricacies of the Windows 10 partition index, exploring its purpose, structure, and implications for system performance and data management.
What is a Partition Index?
The partition index is essentially a directory or a table that resides on your hard drive, specifically within the Master Boot Record (MBR) or the GUID Partition Table (GPT). This index acts as a map, providing the operating system with essential information about the different partitions on your hard drive.
Partitions are logical divisions of your physical hard drive, each serving a specific purpose. For instance, one partition might hold the Windows operating system, another might be dedicated to storing user files, and a third might be designated for backups. The partition index acts as the central point of reference for the operating system, enabling it to locate and access data within these partitions.
The Importance of the Partition Index
The partition index is critical for several reasons:
- Boot Process: When you turn on your computer, the operating system needs to locate the boot partition, which contains the necessary files to initiate the boot process. The partition index provides this crucial information, ensuring a seamless startup.
- Data Management: The partition index allows the operating system to identify and access data stored on different partitions. This enables efficient file management, data retrieval, and program execution.
- Disk Management: The partition index is essential for managing disk space, creating and deleting partitions, and formatting the hard drive. This functionality is critical for optimizing disk usage and ensuring data integrity.
- Data Recovery: In the event of data loss or system failure, the partition index can assist in data recovery efforts. By providing information about the structure of the hard drive, it helps recovery tools identify and retrieve lost data.
The Structure of the Partition Index
The partition index is organized differently depending on whether your computer uses the MBR or GPT partitioning scheme.
- MBR (Master Boot Record): This older scheme uses a partition table located in the first sector of the hard drive. The MBR partition table can store information about up to four primary partitions.
- GPT (GUID Partition Table): This newer scheme uses a partition table located in a dedicated area of the hard drive. GPT offers greater flexibility, allowing for up to 128 partitions and supporting larger hard drives.
Both MBR and GPT partition indexes contain key information about each partition, including:
- Partition Type: Identifies the purpose of the partition, such as "system," "boot," or "data."
- Starting Sector: Specifies the first sector of the partition on the hard drive.
- Ending Sector: Specifies the last sector of the partition on the hard drive.
- Partition Size: Indicates the total size of the partition in bytes.
Understanding the Partition Index in Windows 10
Windows 10 provides several tools for managing partitions and accessing information about the partition index:
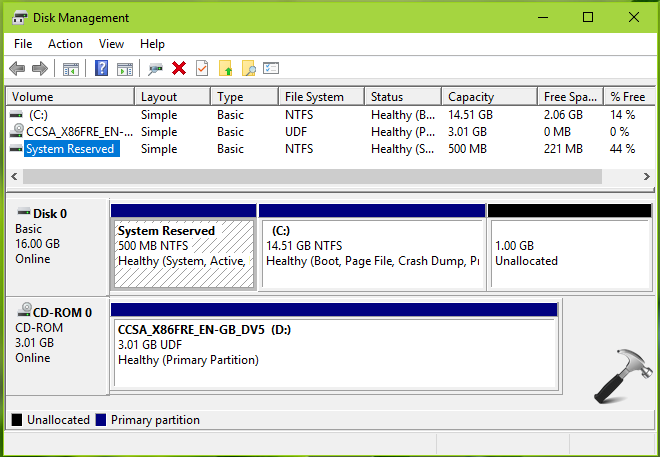
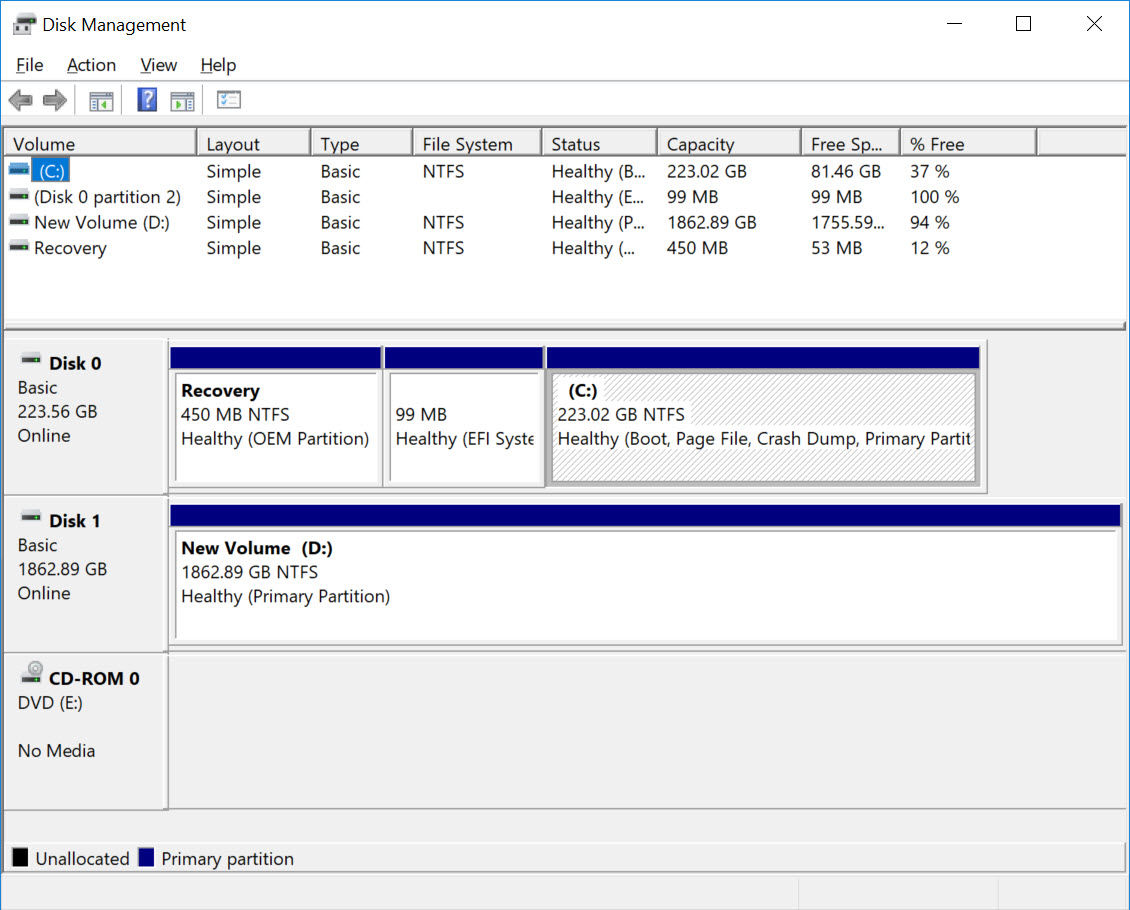
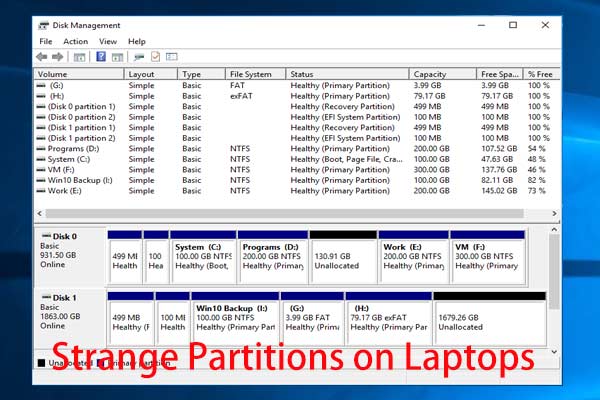
- Disk Management: This built-in tool allows you to view, create, delete, format, and resize partitions. It also displays the partition index information, including partition type, size, and location.
- Command Prompt: Using commands like "diskpart" and "list partition," you can access detailed information about the partition index and manage partitions.
- Third-Party Tools: Numerous third-party tools are available that offer more advanced partition management features, including data recovery, disk cloning, and partition resizing.
Maintaining the Partition Index
While the partition index is generally robust, it can be affected by factors like:
- Software Errors: Faulty software or system crashes can corrupt the partition index, leading to boot issues or data loss.
- Hardware Failures: Hard drive malfunctions or physical damage can compromise the partition index, making it inaccessible or unreliable.
- Improper Partition Management: Incorrectly resizing or deleting partitions can damage the partition index, resulting in data loss or system instability.
It’s crucial to maintain the integrity of the partition index to ensure smooth system operation and data security. Here are some essential tips:
- Regular Backups: Regularly back up your data to prevent data loss in case of system failures or partition index corruption.
- Use Reliable Software: Only use reputable software for partition management and avoid making changes without proper knowledge and understanding.
- Avoid Physical Impact: Protect your hard drive from physical damage to prevent partition index corruption.
- Monitor System Health: Regularly monitor your system for errors and warnings related to the hard drive or partition index.
- Consider Professional Help: If you encounter any issues with your partition index or require advanced partition management, consult a qualified professional.
FAQs about the Windows 10 Partition Index
1. Can I change the partition index manually?
While it’s possible to modify the partition index using specialized tools, it’s not recommended for inexperienced users. Incorrect modifications can lead to data loss or system instability.
2. How can I recover a corrupted partition index?
If your partition index is corrupted, you can attempt to recover it using data recovery software or seek professional assistance. However, data recovery is not always guaranteed, and you may lose some or all of your data.
3. What happens if the partition index is deleted?
Deleting the partition index will render your hard drive inaccessible. The operating system will be unable to locate the partitions, and you will lose access to all data stored on the drive.
4. Can I create a backup of the partition index?
While you can’t directly create a backup of the partition index, you can back up your entire hard drive, which includes the partition index. This will allow you to restore the partition index in case of corruption or loss.
5. Is the partition index affected by defragmentation?
Defragmentation primarily focuses on optimizing file placement on the hard drive and doesn’t directly impact the partition index. However, defragmentation can indirectly improve system performance, which may benefit the overall functionality of the partition index.
6. Can I move the partition index to a different location?
The partition index is typically located in a specific area of the hard drive (MBR or GPT) and cannot be moved to another location. Attempting to do so can lead to severe system issues.
7. What is the difference between the partition index and the file system?
The partition index is a directory or map that helps the operating system locate partitions on the hard drive. The file system, on the other hand, is a hierarchical structure used to organize and manage files within a partition.
8. Can I use the partition index to access data from a different hard drive?
The partition index is specific to the hard drive on which it resides. It cannot be used to access data from other hard drives.
9. How can I check the health of the partition index?
You can check the health of the partition index using the Disk Management tool in Windows 10. If you see any errors or warnings related to the hard drive or partition index, it’s advisable to investigate further.
10. What are the potential consequences of a corrupted partition index?
A corrupted partition index can lead to various issues, including:
- Inability to boot the operating system: The operating system might not be able to locate the boot partition, preventing it from starting.
- Data loss: Data stored on the affected partitions might become inaccessible or corrupted.
- System instability: The operating system might experience frequent crashes or errors due to the corrupted partition index.
- Hardware failures: In some cases, a corrupted partition index might indicate underlying hardware issues with the hard drive.
Conclusion
The partition index is a crucial component of the Windows 10 operating system, playing a vital role in disk management, data access, and system performance. By understanding its purpose, structure, and potential vulnerabilities, users can take proactive steps to maintain its integrity and ensure a stable and reliable computing experience.
While the partition index is generally robust, it’s essential to be aware of its importance and implement preventative measures to safeguard it from corruption or damage. Regular backups, reliable software, and responsible partition management practices are key to minimizing the risk of partition index issues and ensuring the smooth operation of your Windows 10 system.


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Windows 10 Operating System Partition Index: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!