Bypassing Windows 10 Password: A Guide to Registry Modification
Related Articles: Bypassing Windows 10 Password: A Guide to Registry Modification
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Bypassing Windows 10 Password: A Guide to Registry Modification. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Bypassing Windows 10 Password: A Guide to Registry Modification
![How To Bypass Windows 10 Password? [SOLVED]](https://digicruncher.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/chnage-a-password.jpg)
This article delves into a specific technique for altering Windows 10 login behavior, specifically by modifying the Windows Registry. It is crucial to understand that this method is primarily intended for troubleshooting purposes and may not be appropriate for all users. Improper registry modifications can lead to system instability and data loss, so proceeding with caution is paramount.
Understanding the Registry and Its Role in Login Security
The Windows Registry is a central database storing system settings, user profiles, and application configurations. It acts as a comprehensive repository for critical operating system information, impacting various functionalities, including user authentication.
The Potential Risks of Modifying the Registry
While the registry offers a powerful avenue for customizing Windows behavior, it’s essential to be aware of the associated risks. Altering registry entries without proper knowledge can:
- Cause System Instability: Incorrect modifications can disrupt essential system processes, leading to crashes, freezes, or erratic behavior.
- Lead to Data Loss: Critical data stored within the registry can be accidentally deleted or corrupted, resulting in data loss or application malfunctions.
- Compromise Security: Manipulating registry settings related to security can inadvertently weaken system defenses, making it vulnerable to malware or unauthorized access.
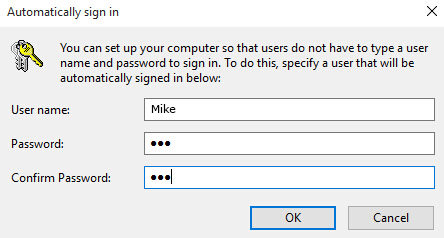
Exploring the "AutoLogon" Registry Setting
One specific registry key, "AutoLogon," enables automatic login to Windows without requiring a password. This setting is typically employed for unattended computers or specific scenarios where manual login is inconvenient. However, its improper use can compromise system security.
Step-by-Step Guide: Modifying the Registry for Automatic Login
Caution: Proceed with extreme caution when modifying the registry. It is recommended to create a system restore point before making any changes.
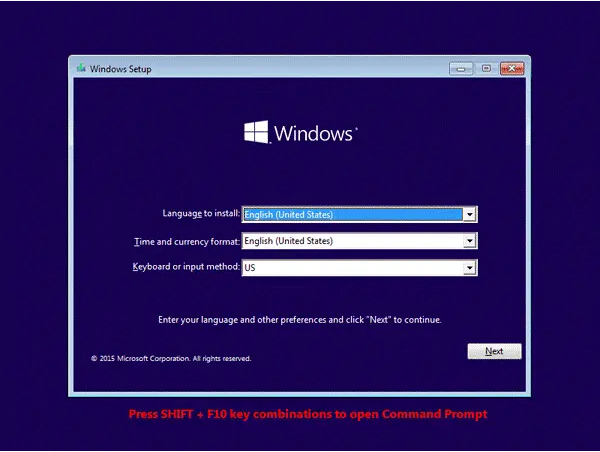
- Access the Registry Editor: Press "Windows key + R" to open the Run dialog box. Type "regedit" and press Enter.
- Navigate to the AutoLogon Key: Locate the following path:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREMicrosoftWindows NTCurrentVersionWinlogon - Create New Values: Right-click within the Winlogon folder and select "New" -> "DWORD (32-bit) Value." Create the following values:
- AutoAdminLogon: Set its value data to "1."
- DefaultUserName: Enter the desired username.
- DefaultPassword: Enter the desired password.
- Apply Changes: Close the Registry Editor and restart your computer.
Important Considerations:
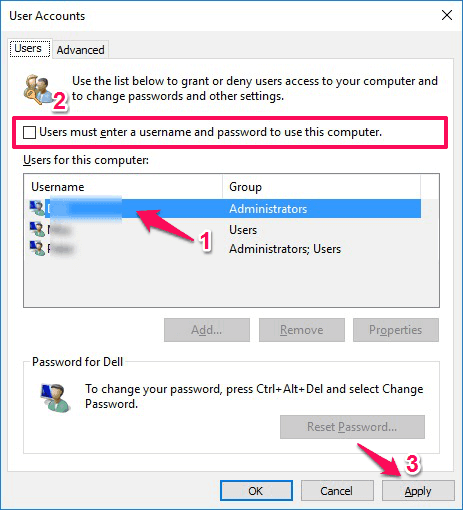
- Security Implications: Disabling password protection weakens system security. Only use this method for specific scenarios and ensure the computer is physically secure.
- Password Visibility: The password entered in the registry is stored in plain text, making it vulnerable if the system is compromised.
- Alternative Solutions: Consider alternative methods for automatic login, such as using a local administrator account with a simple password or utilizing a password manager.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is this method safe for regular use?
A: No, this method is not recommended for regular use. Disabling password protection significantly weakens system security.
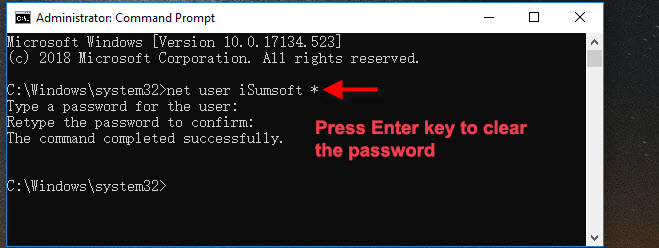
Q: Can I use this method to bypass a forgotten password?
A: No, this method cannot be used to bypass a forgotten password. It requires knowing the existing password.
Q: What are the alternatives to modifying the registry?
A: Alternatives include using a local administrator account with a simple password, utilizing a password manager, or employing a dedicated automatic login tool.
Tips for Secure Login Management
- Strong Passwords: Use complex passwords with a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols.
- Password Manager: Employ a password manager to securely store and manage your passwords.
- Multi-Factor Authentication: Enable multi-factor authentication for critical accounts to add an extra layer of security.
- Regular Updates: Keep your operating system and security software updated to patch vulnerabilities.
- System Restore Point: Create regular system restore points to easily revert to a previous state if issues arise.
Conclusion
While modifying the registry to bypass password protection may seem convenient in certain scenarios, it is crucial to understand the potential risks and security implications. This method should only be employed for troubleshooting purposes and with extreme caution. Implementing secure login practices, such as using strong passwords, multi-factor authentication, and regular system updates, is essential for protecting your data and maintaining a secure computing environment.

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Bypassing Windows 10 Password: A Guide to Registry Modification. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!