Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs
Related Articles: Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs
- 2 Introduction
- 3 Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs
- 3.1 Unveiling the Language of Multimedia: What are Codecs?
- 3.2 The Importance of Codecs: Why They Matter for Your Multimedia Experience
- 3.3 Understanding Windows 10 Media Player’s Built-in Codecs: A Foundation for Multimedia Playback
- 3.4 Expanding Your Media Horizons: Installing Additional Codecs
- 3.5 Navigating Codec Compatibility: A Guide to Seamless Playback
- 3.6 Troubleshooting Playback Issues: Identifying and Resolving Codec Problems
- 3.7 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Windows 10 Media Player Codecs
- 3.8 Tips for Optimizing Your Windows 10 Media Player Codec Experience
- 3.9 Conclusion: Mastering the Language of Multimedia with Windows 10 Media Player Codecs
- 4 Closure
Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs

The Windows 10 Media Player is a versatile tool for enjoying multimedia content, but its functionality hinges on a crucial element: codecs. These software programs act as translators, enabling the player to interpret and display various audio and video formats. Understanding codecs is essential for ensuring a smooth and enjoyable multimedia experience on Windows 10.
Unveiling the Language of Multimedia: What are Codecs?
Imagine a multilingual world where communication requires translators. Codecs play a similar role in the digital world, bridging the gap between the way multimedia data is stored and the way it is presented on your screen.
A codec, short for "coder-decoder," is a set of algorithms that compress and decompress digital media files. Compression reduces file size, making storage and transmission more efficient. Decompression, on the other hand, restores the original data for playback.
The Importance of Codecs: Why They Matter for Your Multimedia Experience
Codecs are the invisible heroes of multimedia playback. Without them, your Windows 10 Media Player would be unable to play most audio and video files. Here’s why they are crucial:
- Enabling Playback: Codecs allow the media player to understand the format of a file, enabling it to decode the data and present it as a playable video or audio stream.
- Ensuring Quality: Different codecs offer varying levels of compression, impacting the quality of the output. High-quality codecs preserve detail and fidelity, while lower-quality codecs may result in some loss of information.
- Supporting Diverse Formats: The multimedia world is filled with diverse formats, each with its own codec. From popular formats like MP4 and AVI to specialized formats like MKV and FLAC, codecs ensure compatibility and playback across a wide range of media.
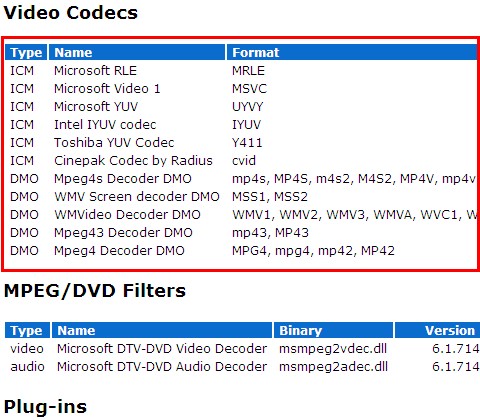
Understanding Windows 10 Media Player’s Built-in Codecs: A Foundation for Multimedia Playback
Windows 10 Media Player comes equipped with a set of built-in codecs that handle a wide range of common multimedia formats. These codecs provide a solid foundation for enjoying most audio and video files without the need for additional installations. However, some specialized formats may require additional codecs to be installed.
Expanding Your Media Horizons: Installing Additional Codecs
While Windows 10 Media Player offers a good selection of built-in codecs, it’s possible that you might encounter a file format that it cannot handle. In these cases, installing additional codecs can expand your multimedia capabilities.
Several sources for additional codecs exist:
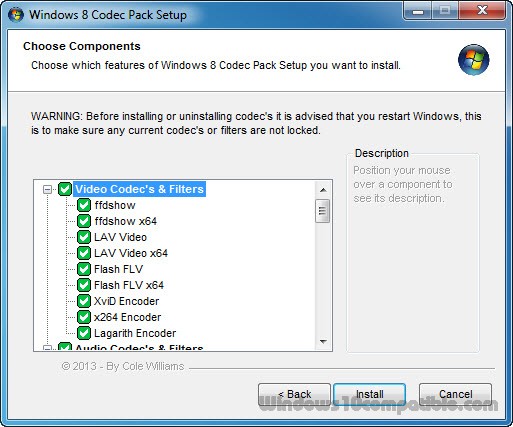
- Software Packages: Many software packages, like VLC Media Player or K-Lite Codec Pack, offer a comprehensive collection of codecs. These packages often include codecs for a vast range of formats, ensuring compatibility with a wide variety of media.
- Individual Codecs: You can also install individual codecs from reputable sources, such as the website of the codec developer. This approach provides more control over the specific codecs you install.
- Windows Update: Windows Update occasionally releases updates that include new codecs, ensuring compatibility with newer formats.
Navigating Codec Compatibility: A Guide to Seamless Playback
When installing additional codecs, it’s essential to ensure compatibility. Installing incompatible codecs can lead to playback issues or even system instability.
Here are some key considerations for codec compatibility:
- Operating System Compatibility: Ensure that the codec is compatible with your version of Windows 10.
- File Format Compatibility: Check that the codec supports the specific file format you wish to play.
- Codec Version Compatibility: Ensure that the codec version is compatible with the Media Player version you are using.
Troubleshooting Playback Issues: Identifying and Resolving Codec Problems
Occasionally, you might encounter playback issues with Windows 10 Media Player. Codec incompatibility is a common culprit.
Here are some steps to troubleshoot playback issues:
- Check for Missing Codecs: If the Media Player cannot play a specific file format, it might be missing the necessary codec.
- Update Codecs: Outdated codecs can lead to playback problems. Updating to the latest version of the codec might resolve the issue.
- Uninstall Conflicting Codecs: Multiple codecs for the same format can sometimes conflict, causing playback issues. Try uninstalling any unnecessary or conflicting codecs.
- Reinstall Media Player: Reinstalling the Media Player can resolve codec-related issues, particularly if they are caused by corrupt codec files.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Windows 10 Media Player Codecs
Q: What are the most common codec formats supported by Windows 10 Media Player?
A: Windows 10 Media Player supports a wide range of common audio and video formats, including:
- Audio: MP3, WMA, AAC, FLAC, ALAC
- Video: MP4, AVI, MKV, WMV, MOV
Q: How can I determine which codecs are installed on my Windows 10 system?
A: You can use the following methods to identify installed codecs:
- Windows Media Player: Open Media Player and go to "Help > About Windows Media Player." The "Codec Information" section lists installed codecs.
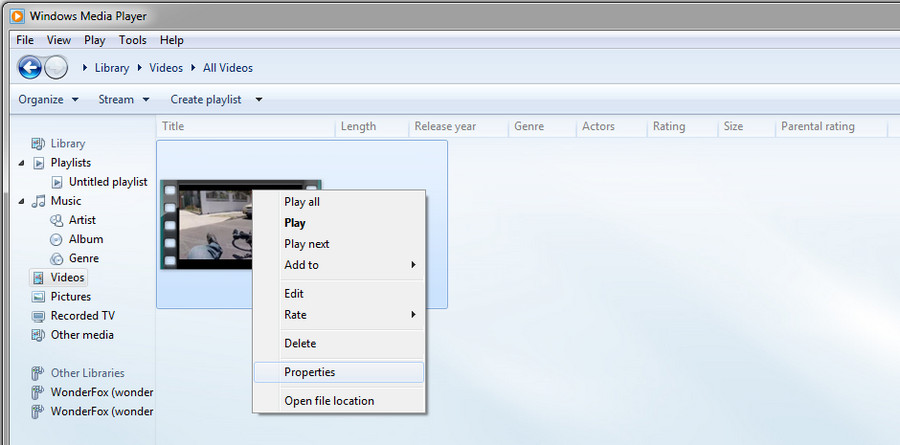
- File Properties: Right-click on a media file and select "Properties." The "Details" tab will show the codec used for the file.
- Third-Party Tools: Some third-party tools, like MediaInfo, can provide detailed codec information about media files.
Q: Can I use a different media player instead of Windows 10 Media Player?
A: Yes, you can use alternative media players like VLC Media Player, KMPlayer, or MPC-HC. These players often come with a broader range of built-in codecs, offering more compatibility with various media formats.
Q: What are some recommended codec packages for Windows 10?
A: Several reputable codec packages are available for Windows 10, including:
- K-Lite Codec Pack: A comprehensive package offering a wide selection of codecs, filters, and tools.
- VLC Media Player: While primarily a media player, VLC also includes a robust set of codecs, providing excellent multimedia compatibility.
- FFmpeg: A powerful command-line tool that can handle a wide range of audio and video formats.
Q: Is it safe to download codecs from unknown sources?
A: Downloading codecs from unknown sources can be risky. It’s recommended to obtain codecs from reputable sources like the codec developer’s website or trusted software packages.
Tips for Optimizing Your Windows 10 Media Player Codec Experience
- Keep Codecs Updated: Regularly update your codecs to ensure compatibility with new media formats and security patches.
- Choose Reputable Sources: Download codecs from reliable sources to minimize the risk of malware or corrupted files.
- Uninstall Unnecessary Codecs: Remove unused or conflicting codecs to prevent potential issues and optimize system performance.
- Use Dedicated Media Players: Consider using specialized media players like VLC or MPC-HC, which often come with a wider range of codecs and advanced features.
- Check for Codec Updates: Regularly check for updates to your installed codec packages or individual codecs to ensure compatibility and security.
Conclusion: Mastering the Language of Multimedia with Windows 10 Media Player Codecs
Codecs are the silent heroes of multimedia playback, enabling Windows 10 Media Player to decode and display a vast array of audio and video formats. Understanding the role of codecs and managing their installation and updates is crucial for ensuring a smooth and enjoyable multimedia experience. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this article, you can unlock the full potential of your Windows 10 Media Player and enjoy a world of multimedia content.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Decoding the Power of Windows 10 Media Player: A Comprehensive Guide to Codecs. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!