Mastering Control: A Deep Dive into Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) ADMX
Related Articles: Mastering Control: A Deep Dive into Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) ADMX
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Mastering Control: A Deep Dive into Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) ADMX. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Mastering Control: A Deep Dive into Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) ADMX
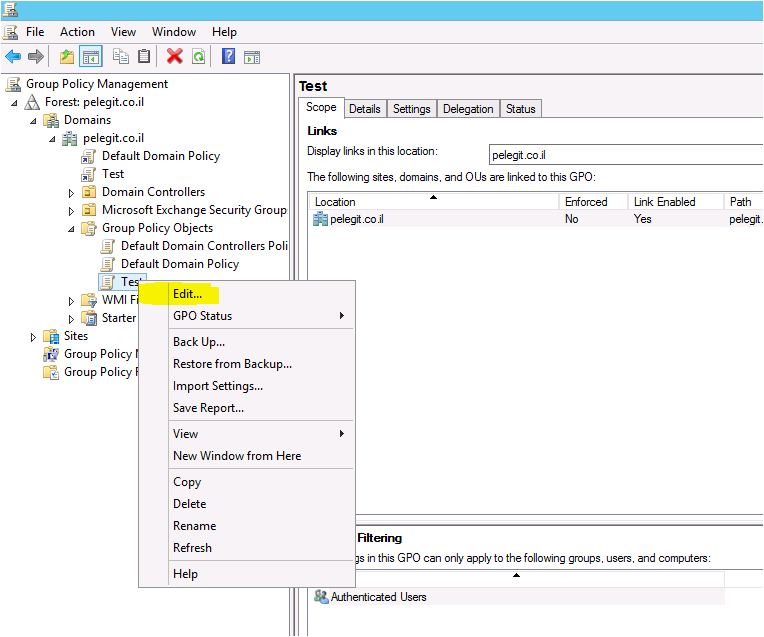
In the intricate world of network administration, maintaining order and ensuring compliance across a multitude of computers can be a daunting task. Thankfully, Windows 10 and 11 offer a robust toolset for centralized management: Group Policy Objects (GPO) and their associated ADMX templates. These powerful mechanisms allow administrators to define and enforce a wide range of settings, from software installations and security configurations to user experience customizations, all within a centralized framework.
Understanding the Fundamentals
At its core, a Group Policy Object (GPO) is a collection of settings that define how a specific group of computers or users should behave. These settings are stored within a directory structure known as the Active Directory (AD), a centralized database that manages users, computers, and other network resources.
ADMX Templates: The Blueprint for Configuration
ADMX templates, essentially XML files, act as the blueprint for defining and organizing the configuration settings within a GPO. They provide a structured framework for configuring various aspects of the Windows operating system, encompassing security, user accounts, network connectivity, software installations, and more.
The Power of Centralized Control
The true power of GPOs and ADMX templates lies in their ability to provide centralized control over a diverse range of settings. Administrators can create and manage these policies within the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC), a graphical interface that simplifies the process.
Benefits of Utilizing GPOs and ADMX Templates
-
Enhanced Security: GPOs enable administrators to enforce security policies across the network, including password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and user rights assignments. This centralized approach helps mitigate security risks and maintain a secure environment.
-
Streamlined Software Deployment: GPOs offer a robust mechanism for software deployment, allowing administrators to push out applications and updates to specific user groups or entire networks. This simplifies software management and ensures consistent application availability across the organization.
-
Improved User Experience: GPOs empower administrators to tailor the user experience by configuring desktop settings, start menu configurations, and other user interface elements. This ensures a consistent and productive environment for all users.
-
Simplified Network Management: GPOs provide a central hub for managing network settings, including DNS configuration, IP address assignments, and network security policies. This streamlined approach simplifies network administration and ensures consistent connectivity across the organization.
-
Enhanced Compliance: GPOs are instrumental in enforcing compliance with industry regulations and internal policies. By configuring settings related to data protection, user access control, and security protocols, organizations can ensure adherence to relevant standards.
A Deeper Dive into ADMX Template Features
ADMX templates are highly customizable, allowing administrators to fine-tune settings to suit their specific needs. Here’s a glimpse into some of their key features:
-
Policy Settings: ADMX templates offer a wide range of policy settings covering various aspects of the Windows operating system, including user accounts, security, network configuration, and software deployment.
-
Configuration Profiles: ADMX templates allow administrators to create configuration profiles, which group related settings into logical units. This simplifies management and ensures consistency in policy application.
-
Predefined Settings: ADMX templates come equipped with predefined settings for common configurations, providing a starting point for customizing policies.
-
Customizable Settings: Administrators can create and modify custom settings to address unique organizational needs, extending the functionality of ADMX templates beyond their default configurations.
-
Policy Inheritance: ADMX templates support policy inheritance, allowing policies to cascade down the organizational hierarchy. This ensures that settings are applied consistently across different levels of the organization.
Navigating the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC)
The Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) provides a user-friendly interface for creating, managing, and deploying GPOs. It offers a hierarchical view of the Active Directory structure, allowing administrators to easily navigate and edit policies.
Key Features of the GPMC:
-
Policy Creation and Editing: The GPMC allows administrators to create new GPOs and modify existing ones, enabling them to customize policy settings according to their specific needs.
-
Policy Linking: The GPMC facilitates the linking of GPOs to specific organizational units (OUs), ensuring that the right policies are applied to the appropriate groups of users and computers.
-
Policy Reporting: The GPMC provides comprehensive reporting capabilities, allowing administrators to track policy application and identify potential issues.
-
Policy Deployment: The GPMC streamlines the deployment of GPOs, ensuring that policies are applied efficiently and effectively across the network.
Best Practices for Effective GPO and ADMX Template Management
-
Plan and Design Carefully: Before implementing GPOs, it’s essential to carefully plan and design the policy structure, considering organizational needs and existing infrastructure.
-
Test Thoroughly: Always test new GPOs in a test environment before deploying them to the production network. This helps identify and resolve potential issues before they impact users.
-
Document Policies: Maintain detailed documentation of all GPOs, including their purpose, configuration settings, and any relevant dependencies. This ensures that policies are easily understood and maintained.
-
Monitor Policy Application: Regularly monitor policy application to ensure that GPOs are working as intended and to identify any potential issues.
-
Implement Change Management: Establish a formal process for managing changes to GPOs, ensuring that changes are properly documented, tested, and approved before deployment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the difference between ADMX and ADM templates?
A: ADM templates, used in older versions of Windows, were text-based files that lacked the flexibility and organization of ADMX templates. ADMX templates, introduced in Windows Server 2008 R2 and Windows 7, utilize XML format, offering enhanced customization and management capabilities.
Q: How do I create a new GPO?
A: To create a new GPO, open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) and navigate to the desired organizational unit (OU). Right-click the OU and select "Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…" Follow the prompts to configure the new GPO.
Q: How do I edit an existing GPO?
A: To edit an existing GPO, locate the desired GPO in the GPMC and right-click it. Select "Edit" to access the policy settings and make the necessary changes.
Q: How do I link a GPO to an OU?
A: In the GPMC, right-click the desired OU and select "Link an existing GPO…" Choose the GPO you want to link to the OU, and click "OK."
Q: How do I deploy a GPO?
A: Once a GPO is created and linked to an OU, it will be automatically deployed to the users and computers within that OU.
Q: What are some common GPO settings?
A: Common GPO settings include password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, software installation rules, network configuration settings, and user interface customizations.
Tips for Efficient GPO Management
-
Use a central repository: Store all ADMX templates in a central location, such as a network share, to ensure easy access and consistent application.
-
Leverage Group Policy Preferences: Group Policy Preferences (GPP) offer a more flexible approach to configuring user settings, allowing administrators to customize settings at the individual user level.
-
Utilize the "Apply Group Policy" command: Use the "gpupdate /force" command to manually refresh policy settings on individual computers, ensuring that changes are applied promptly.
-
Consider third-party tools: Explore third-party tools that can enhance GPO management, providing features like policy auditing, reporting, and automated deployment.
Conclusion
Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) and ADMX templates offer a powerful and versatile mechanism for centralized management, enabling administrators to effectively control and configure various aspects of the operating system. By leveraging these tools, organizations can streamline network administration, enhance security, improve user experience, and ensure compliance with industry regulations. Understanding the fundamentals of GPOs and ADMX templates, along with best practices for their implementation, is crucial for maximizing their effectiveness and ensuring a secure and well-managed network environment.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Mastering Control: A Deep Dive into Windows 10 and 11 Group Policy Objects (GPO) ADMX. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
