The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining
Related Articles: The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
- 1 Related Articles: The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining
- 2 Introduction
- 3 The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining
- 3.1 The Essence of Domain Joining
- 3.2 The Domain Joining Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 3.3 Troubleshooting Common Issues
- 3.4 FAQs About Domain Joining
- 3.5 Tips for Effective Domain Joining
- 3.6 Conclusion: The Importance of Domain Joining
- 4 Closure
The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining
In the realm of computer networks, domain joining stands as a crucial element for organizations seeking to manage and secure their systems effectively. This process allows individual Windows 10 computers to become part of a larger, centrally controlled network structure known as a domain. By integrating into a domain, these computers gain access to shared resources, centralized policies, and enhanced security measures, streamlining operations and bolstering overall network stability.
The Essence of Domain Joining
Imagine a vast network of computers, each functioning independently. While this may seem appealing at first, it quickly becomes cumbersome to manage and maintain. This is where domain joining steps in, offering a centralized solution to handle various aspects of network administration.
Key Benefits of Domain Joining:
- Centralized User Management: Instead of managing individual user accounts on each computer, domain joining enables administrators to create and manage user profiles from a single location. This streamlines user account creation, password management, and access control.
- Simplified Software Deployment: Domain joining empowers administrators to deploy software applications and updates to all computers within the domain simultaneously. This eliminates the need for manual installation on each individual machine, saving valuable time and resources.
- Enhanced Security: Domain policies can enforce strict security measures, such as password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and access restrictions. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Streamlined Resource Sharing: Domain joining facilitates seamless sharing of files, printers, and other resources across the network. Users can easily access shared folders and printers without the need for complex file sharing configurations.
- Simplified Group Policy Management: Domain policies, known as Group Policies, allow administrators to configure various settings and restrictions on all computers within the domain. These policies can be used to enforce specific security protocols, software installations, and desktop customizations.
The Domain Joining Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Domain joining is a straightforward process that involves connecting a Windows 10 computer to an Active Directory domain. Here’s a step-by-step guide to navigate this process:
- Domain Information: Gather the necessary information from your network administrator, including the domain name, the domain controller’s IP address, and the credentials of a user account with domain administrator privileges.
- Network Connection: Ensure the Windows 10 computer is connected to the network where the domain resides.
- Access System Properties: Open the "System" settings by pressing the Windows key + X and selecting "System."
- Navigate to "About": In the System window, click on "About" on the left-hand side.
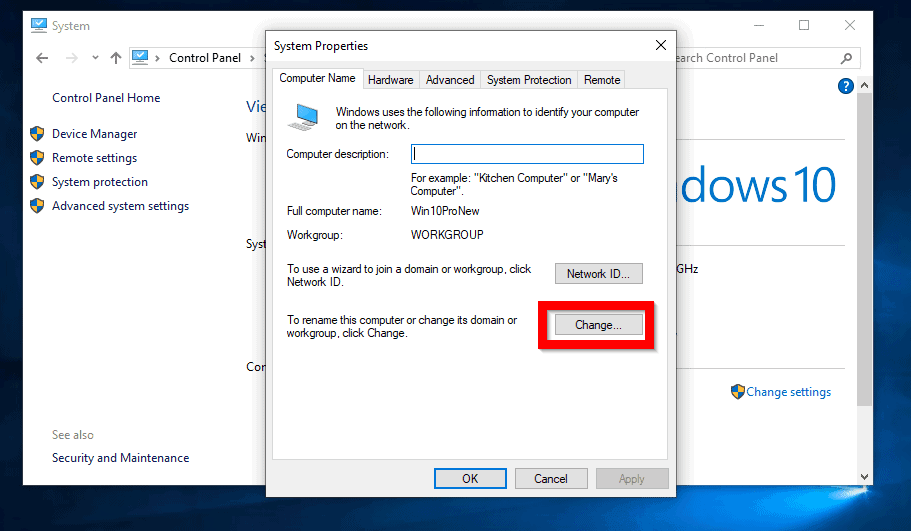
- Locate "Change settings": Scroll down to the "Related settings" section and click on "Change settings" next to "System."
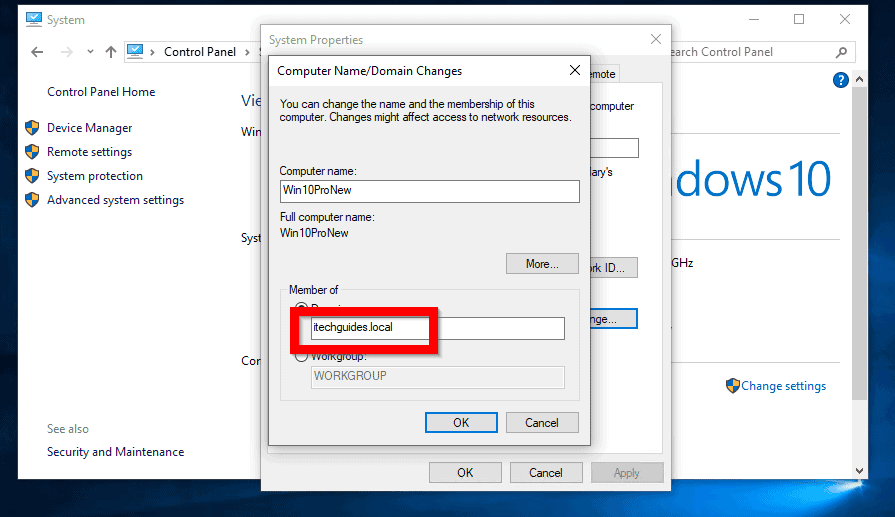
- Access "Computer name, domain, and workgroup settings": In the "System Properties" window, navigate to the "Computer Name" tab.
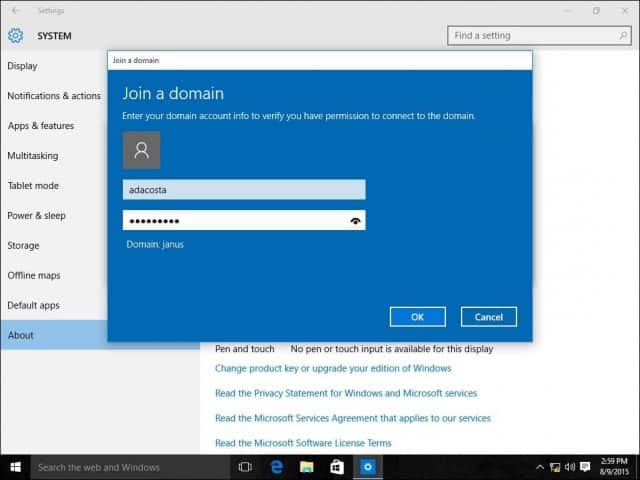
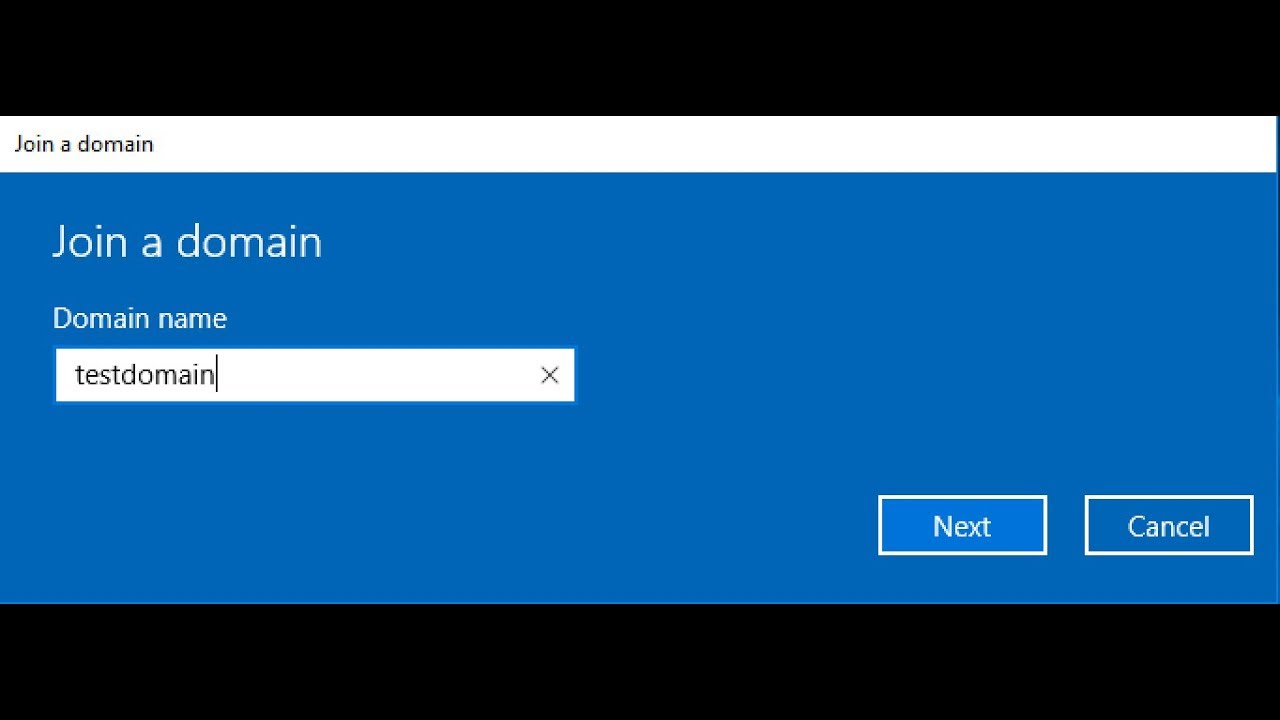
- Join the Domain: Click on the "Change" button and select "Domain." Enter the domain name in the provided field and click "Next."
- Enter Credentials: Provide the username and password of a user account with domain administrator privileges. Click "OK" to proceed.
- Domain Verification: The system will attempt to connect to the domain. If successful, the computer will be added to the domain.
- Restart: Restart the computer to complete the domain joining process.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
While domain joining is generally straightforward, you may encounter some common issues during the process. Here are some troubleshooting tips:
- Incorrect Domain Information: Ensure the domain name, domain controller’s IP address, and administrator credentials are accurate.
- Network Connectivity: Verify the network connection between the computer and the domain controller.
- Firewall Issues: Temporarily disable the firewall on the computer to rule out any interference.
- DNS Configuration: Check the DNS settings on the computer to ensure they correctly point to the domain controller.
- Account Permissions: Confirm that the user account used for domain joining has sufficient administrator privileges.
- Domain Controller Availability: Ensure the domain controller is available and functioning correctly.
FAQs About Domain Joining
1. What is the difference between a workgroup and a domain?
A workgroup is a collection of computers that share resources directly, without a central authority. In contrast, a domain is a centralized network structure managed by an Active Directory server, offering centralized user management, security policies, and resource sharing.
2. Can I join multiple domains with a single computer?
No, a Windows 10 computer can only be joined to a single domain at a time.
3. What happens if I leave a domain?
Leaving a domain removes the computer from the central management and security policies of the domain. The computer will revert to its original workgroup settings.
4. Can I join a domain without administrator privileges?
No, joining a domain requires administrator privileges on the target computer.
5. Is domain joining mandatory for all Windows 10 computers?
Domain joining is not mandatory for all Windows 10 computers. However, it is highly recommended for organizations seeking centralized management, enhanced security, and simplified resource sharing.
Tips for Effective Domain Joining
- Thorough Planning: Before joining a domain, carefully plan the user accounts, group policies, and resource sharing configurations.
- Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation of the domain joining process, including the domain name, domain controller’s IP address, administrator credentials, and any relevant configuration details.
- Regular Maintenance: Regularly update and maintain the domain controller and the computers within the domain to ensure optimal performance and security.
- Security Best Practices: Implement strong security measures, such as password complexity requirements, account lockout policies, and access restrictions, to protect the domain from unauthorized access.
- Backup and Recovery: Regularly back up the domain controller and the computers within the domain to ensure data recovery in case of system failure.
Conclusion: The Importance of Domain Joining
Domain joining stands as a cornerstone of effective network management, offering a centralized solution for user management, security enforcement, and resource sharing. By integrating Windows 10 computers into a domain, organizations can streamline operations, enhance security, and optimize resource utilization. The benefits of domain joining far outweigh the initial setup and configuration efforts, making it an indispensable tool for managing and securing modern computer networks.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Power of Integration: Understanding Windows 10 Domain Joining. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!