Troubleshooting Windows 10 Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Troubleshooting Windows 10 Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Troubleshooting Windows 10 Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide
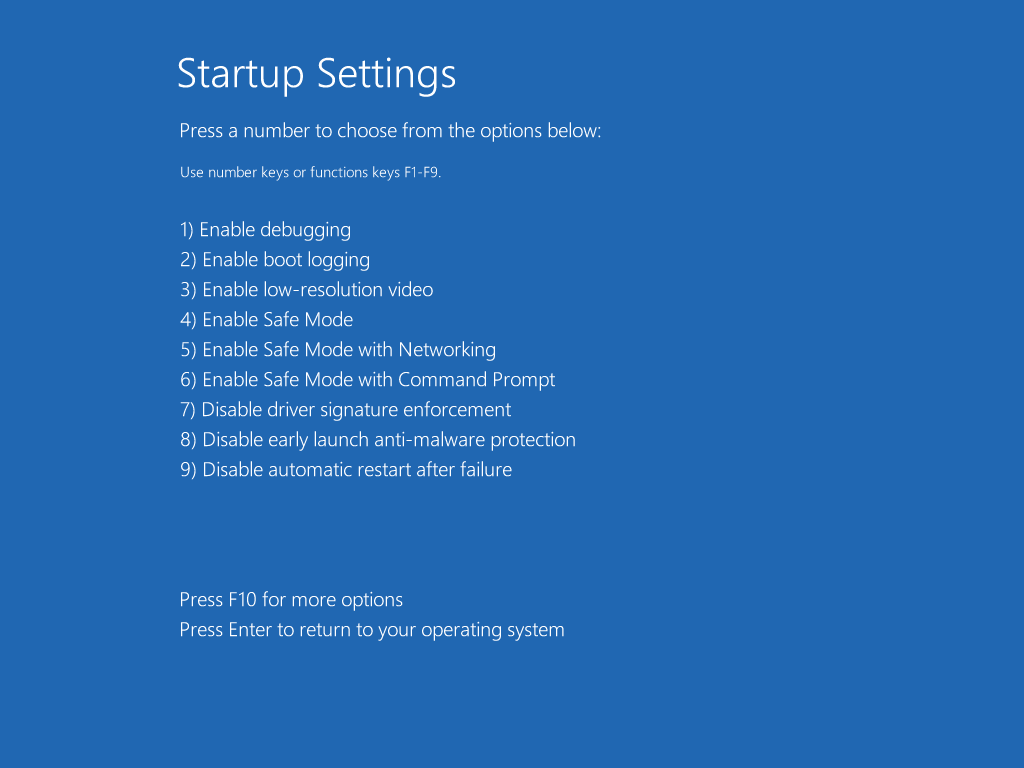
Safe Mode is a critical diagnostic tool in Windows 10, enabling users to troubleshoot and resolve system issues that prevent the operating system from booting normally. This mode starts Windows with a minimal set of drivers and services, effectively isolating potential conflicts and malfunctions. However, encountering difficulties in accessing Safe Mode can be frustrating, hindering troubleshooting efforts and leaving users stranded with a malfunctioning system.
Understanding the Importance of Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a vital resource for addressing a range of Windows 10 issues, including:
- Driver Conflicts: Faulty or incompatible device drivers can lead to system instability, crashes, or even the inability to boot. Safe Mode allows users to disable or update drivers, identifying and resolving the source of the conflict.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can interfere with system processes and hinder normal operation. Safe Mode provides a clean environment for running anti-malware scans, removing the threat and restoring system functionality.
- System File Corruption: Critical system files may become damaged or corrupted, preventing Windows 10 from booting properly. Safe Mode allows users to run system file checks and repair corrupted files, restoring the system to a functional state.
- Software Conflicts: Incompatible or faulty software installations can disrupt normal system operation. Safe Mode enables users to uninstall problematic software, resolving conflicts and restoring stability.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Hardware issues can also contribute to boot problems. Safe Mode can help isolate hardware failures by running the system with minimal hardware dependencies.
Common Causes of Safe Mode Access Issues
Several factors can prevent Windows 10 from booting into Safe Mode, including:
- Faulty or Corrupted Drivers: Driver issues can interfere with the boot process, preventing access to Safe Mode.
- Malware Interference: Malicious software can manipulate system processes, blocking access to Safe Mode.
- System File Corruption: Damaged or corrupted system files can disrupt the boot process, hindering Safe Mode access.
- Hardware Malfunctions: Hardware failures, such as a failing hard drive or RAM issues, can cause boot problems and prevent Safe Mode access.
- Boot Configuration Errors: Incorrect boot settings or corrupted boot files can lead to booting difficulties, including Safe Mode access issues.
Troubleshooting Steps: Addressing Safe Mode Boot Issues
Navigating these issues requires a systematic approach. Here’s a comprehensive guide to resolving Windows 10 Safe Mode boot problems:
1. Advanced Startup Options:
- Access the Advanced Startup Options: Restart your computer and repeatedly press the F8 key during the boot process. This should open the Advanced Boot Options menu.
- Select Safe Mode: Use the arrow keys to navigate to "Safe Mode" and press Enter. If this option is unavailable, proceed to the next steps.
2. Using the System Configuration Utility:
- Access the System Configuration Utility: Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box. Type "msconfig" and press Enter.
- Navigate to the Boot Tab: In the System Configuration window, select the "Boot" tab.
- Enable Safe Boot: Check the box next to "Safe boot."
- Select the Desired Safe Mode: Choose the specific Safe Mode variant you require (minimal, network, or command prompt) from the "Boot options" section.
- Apply Changes and Restart: Click "Apply" and then "OK." Restart your computer.
3. Utilizing the Command Prompt:
- Access the Command Prompt: Use the Advanced Startup Options method (F8 during boot) to access the "Command Prompt" option.
- Repair Boot Files: Execute the following command: "bootrec /fixmbr". This command repairs the Master Boot Record, which can resolve boot issues.
- Rebuild Boot Configuration: Execute the following command: "bootrec /fixboot". This command rebuilds the boot configuration data, addressing potential errors.
- Scan for Corrupted Files: Execute the following command: "sfc /scannow". This command scans for and repairs corrupted system files.
4. Using a Bootable USB Drive:
- Create a Bootable USB Drive: Download a bootable USB drive creation tool from a reputable source like Microsoft or Rufus.
- Install Windows 10: Follow the on-screen instructions to create a bootable USB drive and install Windows 10.
- Choose Repair Options: During the installation process, select "Repair your computer" instead of installing Windows 10.
- Troubleshoot and Repair: Use the troubleshooting options provided to repair system files, reset your computer, or restore from a backup.
5. Consider a Clean Installation:
- Backup Your Data: Before proceeding, ensure you have a backup of all important data.
- Format the Hard Drive: Format the hard drive and install a fresh copy of Windows 10.
- Install Drivers and Software: After installation, install necessary drivers and software.
FAQs: Addressing Common Safe Mode Boot Questions
1. What if Safe Mode with Networking is not available?
If Safe Mode with Networking is unavailable, you may need to use a bootable USB drive to access the command prompt and run system file repairs.
2. What if I cannot access the Advanced Startup Options?
If you cannot access the Advanced Startup Options menu, try using a bootable USB drive or a system repair disc to access troubleshooting options.
3. What should I do if my computer keeps restarting?
A constantly restarting computer can indicate a serious issue. Try accessing the Advanced Startup Options menu and selecting "Startup Repair" or "System Restore" to address the problem.
4. Can I access Safe Mode without restarting my computer?
No, accessing Safe Mode requires restarting the computer.
5. What if Safe Mode is still not working after trying all these steps?
If Safe Mode remains inaccessible, you may need to consider a clean installation of Windows 10 or consult a qualified technician for further assistance.
Tips for Preventing Future Safe Mode Issues
- Regularly Update Drivers: Keep your device drivers up-to-date to ensure compatibility and stability.
- Run Anti-malware Scans: Regularly scan your system for malware to prevent infections that can disrupt system processes.
- Backup Your Data: Regularly back up your data to ensure you have a safe copy in case of system failure.
- Monitor System Health: Use system monitoring tools to identify potential issues and address them proactively.
- Avoid Installing Untrusted Software: Only install software from trusted sources to minimize the risk of malware infections.
Conclusion
Navigating Windows 10 Safe Mode issues can be challenging, but a systematic approach and understanding of the underlying causes can help resolve them. From troubleshooting boot configuration errors to addressing driver conflicts and malware infections, the steps outlined in this guide provide a comprehensive framework for regaining access to Safe Mode and restoring your system to a functional state. Remember to always prioritize data backup and seek professional assistance when necessary. By understanding the importance of Safe Mode and implementing preventive measures, you can minimize the risk of future boot issues and ensure a smooth and stable Windows 10 experience.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Troubleshooting Windows 10 Safe Mode: A Comprehensive Guide. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!