Understanding the Foundation of Windows 10: A Deep Dive into NTFS
Related Articles: Understanding the Foundation of Windows 10: A Deep Dive into NTFS
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Foundation of Windows 10: A Deep Dive into NTFS. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Foundation of Windows 10: A Deep Dive into NTFS
The Windows operating system, in its various iterations, has been a dominant force in the world of personal computing for decades. At the heart of this dominance lies a robust and versatile file system: NTFS (New Technology File System). Introduced with Windows NT 3.1 in 1993, NTFS has evolved alongside Windows, becoming the default file system for Windows 10. Its sophisticated design empowers users with a multitude of features, ensuring data integrity, security, and efficient storage management.
The Evolution of a File System
Prior to NTFS, the dominant file system for Windows was FAT (File Allocation Table). While FAT served its purpose, it lacked the advanced features and capabilities that modern operating systems demanded. NTFS, on the other hand, addressed these limitations by introducing a more structured and efficient approach to data organization.
Key Features of NTFS
- Data Integrity: NTFS employs a journaling system, ensuring that file system operations are recorded in a log. This log allows for data recovery in the event of system crashes or unexpected shutdowns, minimizing data loss.
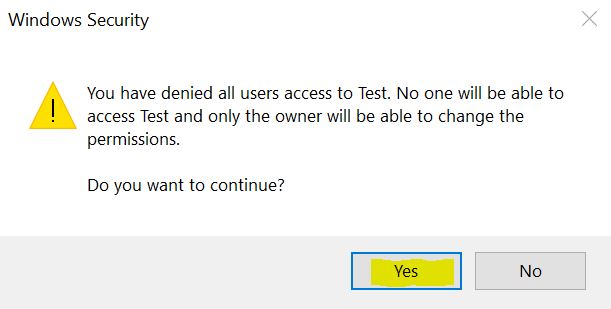
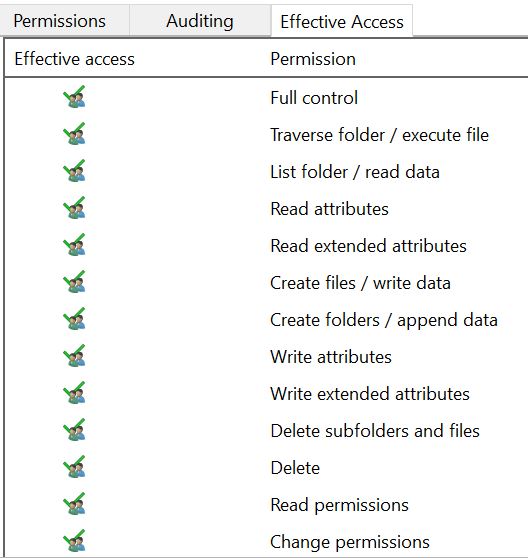
- Security: NTFS implements robust access control lists (ACLs) that allow for fine-grained permissions management. Users and groups can be granted specific permissions, ensuring data security and preventing unauthorized access.
- Advanced File Attributes: NTFS offers a wide range of file attributes, including compression, encryption, and indexing, enhancing data management and optimization.
- Large File and Disk Support: NTFS can handle significantly larger files and disks compared to FAT, catering to the ever-increasing storage needs of modern applications and data.
- Efficient File System Management: NTFS employs a sophisticated allocation scheme, optimizing disk space usage and improving overall system performance.
Delving Deeper into NTFS Features
1. Journaling: The journaling feature in NTFS is a cornerstone of its reliability. Every file system operation is recorded in a log file, creating a history of changes. In case of unexpected system failure, the log can be used to restore the file system to a consistent state, minimizing data loss. This feature is particularly valuable for users who work with critical data or have experienced data corruption in the past.
2. Access Control Lists (ACLs): NTFS’s robust security features are built upon ACLs. These lists define permissions for users and groups, allowing administrators to control who can access and modify files and folders. This granular control helps to prevent unauthorized access and data breaches, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
3. File Compression: NTFS supports compression for individual files and folders, reducing disk space usage and improving performance. This is particularly beneficial for users with limited storage space or those who frequently work with large files.
4. File Encryption: NTFS offers built-in encryption capabilities, allowing users to encrypt individual files or entire volumes. This feature provides an additional layer of security, protecting sensitive data from unauthorized access.
5. Hard Links and Symbolic Links: NTFS supports both hard links and symbolic links, providing flexibility in file management. Hard links create multiple references to the same file data, while symbolic links create shortcuts that point to other files or folders. These features are essential for advanced users who need to manage files efficiently and optimize storage space.
6. File System Metadata: NTFS stores extensive metadata about files, including creation date, modification date, access time, and file attributes. This metadata is used by the operating system and applications to manage and organize files effectively.
7. Disk Space Management: NTFS employs a sophisticated allocation scheme that optimizes disk space usage. This scheme ensures that files are stored efficiently, minimizing fragmentation and improving overall system performance.
Benefits of NTFS for Windows 10 Users
The benefits of NTFS extend beyond its technical features, impacting the user experience in a variety of ways.
- Improved System Performance: NTFS’s efficient file management, data organization, and disk space optimization lead to faster system boot times, quicker application loading, and overall smoother performance.
- Enhanced Data Security: The robust security features, including ACLs and encryption, ensure that user data is protected from unauthorized access and manipulation.
- Increased Reliability: The journaling system minimizes data loss in case of system crashes or unexpected shutdowns, providing peace of mind for users who rely on their data for work, personal projects, or entertainment.
- Flexible File Management: The advanced file attributes, including compression, encryption, and hard/symbolic links, empower users with greater control over their data, allowing for efficient storage management and customization.
Addressing Common Concerns
1. NTFS vs. FAT32: While FAT32 remains a viable option for some use cases, NTFS offers a significant advantage in terms of features, security, and performance. The larger file size and disk support of NTFS make it a more suitable choice for modern systems.
2. NTFS and Disk Space: NTFS’s sophisticated allocation scheme optimizes disk space usage, but it’s essential to manage storage effectively to avoid running out of space. Regularly deleting unnecessary files and using compression or cloud storage solutions can help optimize disk space.
3. Compatibility Issues: While NTFS is the default file system for Windows 10, some older operating systems or devices may not fully support NTFS. In such cases, it may be necessary to format a drive with FAT32 or use a third-party tool to access NTFS volumes.
FAQs about NTFS
Q: What is the difference between NTFS and FAT32?
A: NTFS offers significantly more features and capabilities compared to FAT32, including larger file and disk support, robust security features, and advanced file attributes. FAT32 is primarily used for older operating systems and devices that lack NTFS compatibility.
Q: Can I convert a FAT32 drive to NTFS?
A: Yes, you can convert a FAT32 drive to NTFS using the built-in Disk Management tool in Windows. However, this process will erase all data on the drive, so it’s essential to back up your data before proceeding.
Q: Is NTFS compatible with Mac OS X?
A: While Mac OS X can read NTFS volumes, it cannot write to them by default. You’ll need a third-party tool to enable write access to NTFS volumes from Mac OS X.
Q: Can I use NTFS on a USB drive?
A: Yes, you can format a USB drive with NTFS. This allows for larger file sizes and greater security compared to FAT32. However, ensure that the device you intend to use the USB drive with supports NTFS.
Q: What are the best practices for using NTFS?
A: To optimize NTFS performance and ensure data integrity, it’s recommended to:
- Defragment the drive regularly: This helps to optimize file placement and improve performance.
- Run a check disk scan: This helps to identify and repair errors in the file system.
- Back up your data regularly: This ensures that you have a copy of your important data in case of system failure or data loss.
Tips for Managing NTFS
- Use Disk Management for partition management: The built-in Disk Management tool in Windows allows you to create, resize, and format partitions on your hard drive.
- Utilize compression for large files: NTFS’s compression feature can significantly reduce disk space usage for large files.
- Take advantage of encryption for sensitive data: Encrypting files or entire volumes provides an extra layer of security for sensitive data.
- Monitor disk space usage: Regularly monitor your disk space to avoid running out of space and ensure optimal system performance.
Conclusion
NTFS stands as a testament to the evolution of file systems, offering a robust, secure, and efficient foundation for Windows 10. Its advanced features, including journaling, access control, compression, and encryption, provide users with a powerful toolkit for managing data, ensuring integrity, and safeguarding privacy. By understanding the intricacies of NTFS and applying best practices for its management, users can unlock the full potential of their Windows 10 systems, maximizing performance, security, and data management capabilities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Foundation of Windows 10: A Deep Dive into NTFS. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!