Understanding Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS)
Related Articles: Understanding Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS)
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS). Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS)
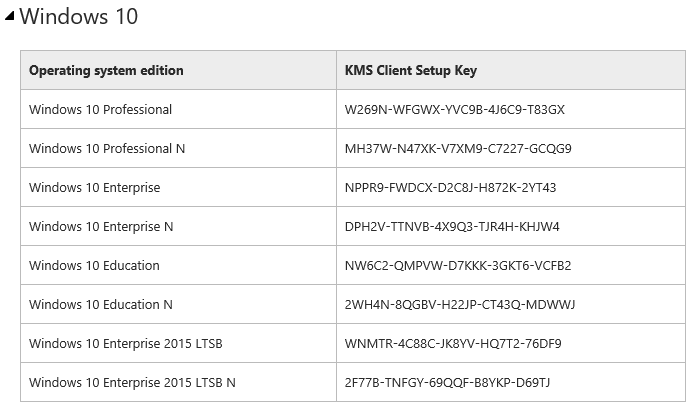
The Windows 10 operating system, like its predecessors, requires a valid license for legal use. This license ensures access to updates, support, and guarantees the software’s legitimacy. One method for managing these licenses within an organization is through the Key Management System (KMS).
What is KMS?
KMS is a licensing mechanism for Windows 10 and other Microsoft products that enables organizations to activate their software in a centralized manner. It acts as a server that stores and manages license keys, allowing clients to activate their software by connecting to the KMS server.
How Does KMS Work?
KMS operates on a client-server model. The KMS server, typically a Windows server, stores the license keys and manages activation requests. Client computers, running Windows 10, connect to the KMS server to activate their licenses.
KMS Activation Process:
- Installation: The KMS server is installed and configured on a designated server within the organization’s network.
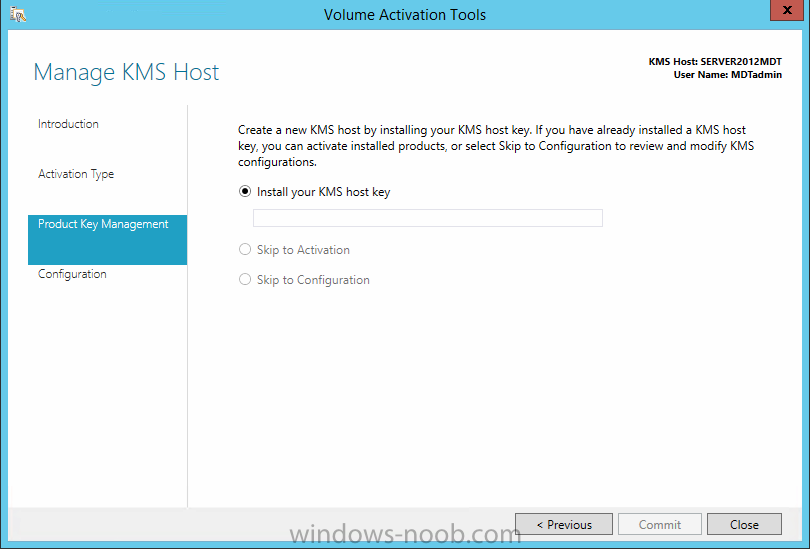
- Key Installation: The KMS host key, a unique key provided by Microsoft, is installed on the KMS server.
- Client Activation: Client computers running Windows 10 connect to the KMS server for activation.
- License Validation: The KMS server verifies the client’s request and checks if the client’s hardware meets the activation requirements.
- Activation Grant: If the validation is successful, the KMS server grants a temporary activation to the client.
- Renewal: The activation granted to the client is temporary and needs to be renewed periodically. This renewal process is typically automatic and happens in the background.
Benefits of Using KMS:
- Centralized License Management: KMS simplifies the activation process by allowing organizations to manage licenses centrally, reducing administrative overhead.
- Simplified Activation: Clients can activate their software without requiring individual product keys, simplifying the activation process.
- Reduced Costs: KMS can potentially reduce licensing costs for organizations with a significant number of computers.
- Enhanced Security: KMS helps prevent unauthorized use of software by ensuring all activations are managed through a central system.
KMS vs. Retail Licensing:
While KMS is a suitable option for organizations, retail licensing is more appropriate for individual users or small businesses. Retail licenses are typically purchased individually and provide permanent activation for a single device.
KMS Requirements:
To implement KMS, organizations need to meet certain requirements:
- Operating System: The KMS server needs to run a supported version of Windows Server.
- Network Connectivity: The KMS server and client computers must be connected to the same network for activation to occur.
- Minimum Client Count: A minimum number of client computers is required to activate the KMS server. This number varies depending on the product being activated.
- Domain Join: KMS servers are typically joined to an Active Directory domain to facilitate efficient license management.
FAQs about Windows 10 KMS:
Q: What is the difference between a KMS key and a Retail key?
A: A KMS key is designed for use with KMS servers and is used to activate multiple clients within an organization. A retail key is intended for individual use and activates a single device permanently.
Q: Can I use KMS to activate my home computer?
A: KMS is not intended for home use and is primarily designed for organizations. You would need a retail license to activate a home computer.
Q: How often does KMS activation need to be renewed?
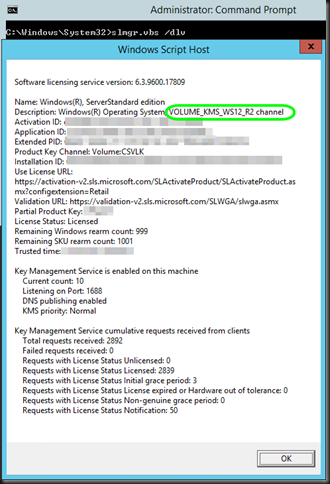
A: KMS activation is typically renewed every 180 days for Windows 10.
Q: Can I use a KMS key for multiple products?
A: No, each KMS key is specific to a particular product, such as Windows 10, and cannot be used for other products.
Q: What happens if my KMS server goes down?
A: If the KMS server is unavailable, clients will not be able to renew their activations. This can result in the client’s license expiring and requiring manual activation.
Tips for Implementing KMS:
- Plan Carefully: Before implementing KMS, ensure you have a clear understanding of your organization’s licensing needs and requirements.
- Choose a Suitable Server: Select a server that meets the KMS requirements and has sufficient resources to handle activation requests.
- Configure KMS Server: Configure the KMS server correctly, ensuring it is joined to the domain and the KMS host key is installed.
- Monitor Activation Status: Regularly monitor the KMS server to ensure it is functioning correctly and clients are successfully activating.
- Implement Backup Strategies: Create a backup of the KMS server to minimize downtime in case of server failure.
Conclusion:
The Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS) provides a centralized and efficient method for managing software licenses within organizations. By understanding the benefits, requirements, and best practices associated with KMS, organizations can effectively manage their Windows 10 licenses, ensuring compliance and minimizing administrative overhead.
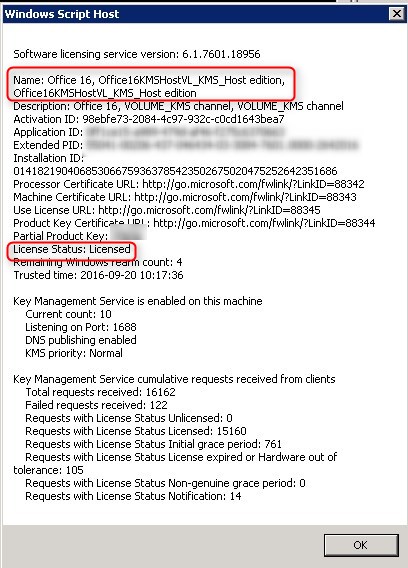

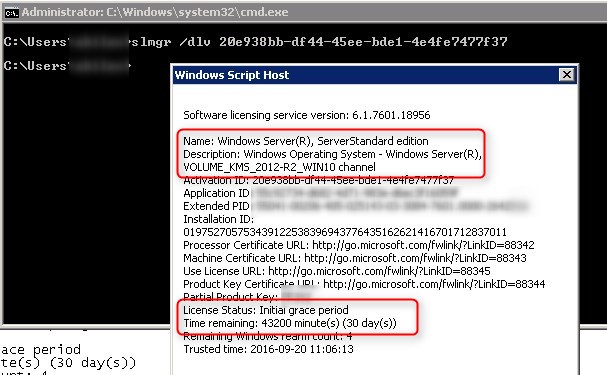


Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Windows 10 Key Management System (KMS). We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!