Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Comprehensive Guide

The familiar Windows 10 logo, a beacon of digital productivity, can unexpectedly turn into a frustrating symbol of system failure. When your computer refuses to boot properly, it can disrupt your workflow, leaving you stranded and seeking solutions. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the common causes behind Windows 10 boot failures, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to diagnose and resolve these issues effectively.
Understanding the Boot Process: A Foundation for Troubleshooting
Before diving into the specifics of boot failures, it is essential to understand the fundamental steps involved in the Windows 10 boot process. This sequence of events, executed upon powering on your computer, orchestrates the loading of the operating system and its associated components:
-
Power-On Self Test (POST): This initial phase involves a hardware check, verifying the integrity of essential components like the motherboard, RAM, and hard drive. Errors detected during POST are usually indicated by beeps or error codes.
-
BIOS/UEFI Initialization: The Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) is loaded, responsible for managing the system’s hardware and initiating the boot process.
-
Boot Device Selection: The BIOS/UEFI identifies and prioritizes the boot devices, typically the hard drive or a USB drive.
-
Boot Loader Execution: The boot loader, a program stored on the boot device, loads the operating system’s kernel and initial files.
-
Operating System Initialization: Windows 10 takes control, loading essential drivers, services, and user interface elements.
Unveiling the Culprits Behind Windows 10 Boot Failures
Now that we have a basic understanding of the boot process, let’s delve into the common culprits responsible for Windows 10 boot failures:
1. Hardware Malfunctions:
- Hard Drive Issues: A failing hard drive can lead to corrupted boot files or inability to access the operating system. Symptoms include clicking noises, slow performance, and frequent crashes.
- RAM Errors: Faulty RAM modules can cause system instability and prevent the boot process from completing successfully.
- Motherboard Problems: Malfunctioning components on the motherboard, such as the chipset or southbridge, can disrupt the boot process.
- Loose Connections: Ensure all cables, including power, data, and RAM modules, are securely connected.
2. Software Glitches:
- Corrupted Boot Files: Essential boot files, such as the Boot Configuration Data (BCD) or Windows Registry, can become corrupted due to software errors, power outages, or malware infections.
- Driver Conflicts: Incompatible or outdated drivers can interfere with the boot process, leading to system instability and crashes.
- Malware Infections: Malicious software can disrupt the boot process by modifying system files, corrupting the boot sector, or hijacking the boot loader.
- Recent Software Changes: Installing new programs or updates can sometimes introduce conflicts or errors that interfere with the boot process.
3. System Configuration Errors:
- Incorrect Boot Order: The BIOS/UEFI boot order might be configured incorrectly, preventing the system from booting from the intended device.
- Disabled Boot Options: Essential boot options, such as Secure Boot or Legacy Boot, might be disabled, preventing the system from booting properly.
- Conflicting BIOS/UEFI Settings: Incompatible or conflicting BIOS/UEFI settings can disrupt the boot process.
4. External Factors:
- Power Surges: Unstable power supply or power surges can damage hardware components or corrupt system files, leading to boot failures.
- Overheating: Excessive heat can damage hardware components, including the hard drive, CPU, and motherboard, causing boot issues.
- Physical Damage: Physical damage to the computer, such as a dropped laptop or a spilled drink, can disrupt the boot process.
Troubleshooting Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Step-by-Step Guide
Once you have a general understanding of the potential causes, it’s time to embark on a systematic troubleshooting journey. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you diagnose and resolve Windows 10 boot failures:
1. Initial Checks:
- Power Cycle: Begin by restarting your computer. This simple step often resolves temporary glitches and can allow the system to boot properly.
- Check for Physical Damage: Inspect your computer for any visible damage or loose connections.
- Monitor for Error Messages: Pay close attention to any error messages displayed during the boot process. These messages can provide valuable clues about the root cause of the issue.
2. Hardware Diagnostics:
- Run BIOS/UEFI Diagnostics: Access the BIOS/UEFI setup menu and run the built-in diagnostics. These tests can help identify hardware failures, such as RAM errors or hard drive problems.
- Test RAM Modules: If the BIOS/UEFI diagnostics indicate a RAM issue, try removing and reseating each RAM module individually. You can also test the RAM modules in another computer to confirm their functionality.
- Check Hard Drive Health: Use a hard drive diagnostic tool, such as CrystalDiskInfo or SeaTools, to assess the health of your hard drive. If the tool reports errors or warnings, consider replacing the drive.
3. Software Troubleshooting:
- Boot into Safe Mode: Safe Mode starts Windows 10 with a minimal set of drivers and services, allowing you to troubleshoot software issues without encountering conflicts.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): This tool scans for and repairs corrupted system files, including those critical for the boot process.
- Perform a Clean Boot: This process starts Windows 10 with a minimal set of drivers and services, helping you identify and resolve software conflicts that might be causing boot issues.
- Restore System to an Earlier Point: If the problem arose after installing a new program or update, restoring your system to an earlier point can revert the changes and potentially resolve the issue.
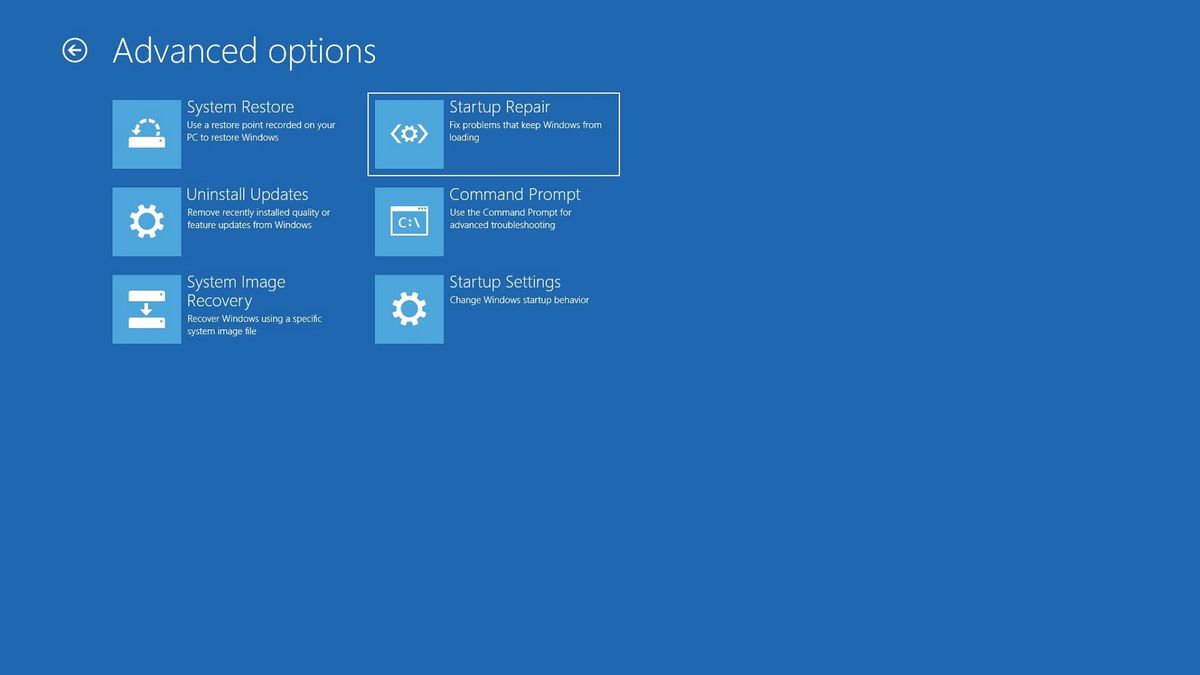
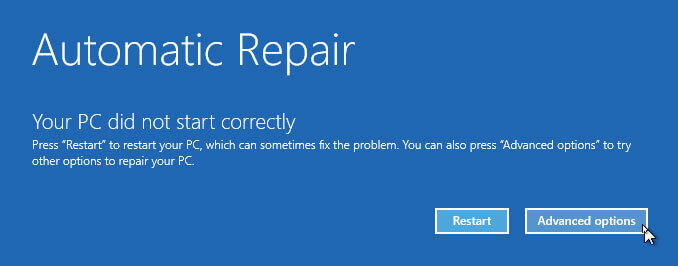
- Use a Startup Repair Tool: Windows 10 includes a built-in Startup Repair tool that can automatically diagnose and fix common boot problems.
- Run a Malware Scan: If you suspect a malware infection, run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program.
4. System Configuration Adjustments:
- Check Boot Order: Access the BIOS/UEFI setup menu and ensure that the boot order is correctly configured, prioritizing the hard drive as the boot device.
- Enable/Disable Boot Options: Review the BIOS/UEFI settings for options related to Secure Boot, Legacy Boot, and other boot-related settings. Ensure these options are configured appropriately for your system.
- Reset BIOS/UEFI Settings: If you have made recent changes to the BIOS/UEFI settings, resetting them to their default values can sometimes resolve boot issues.
5. Advanced Recovery Options:
- Use a Windows 10 Installation Media: If the above troubleshooting steps fail, you can use a Windows 10 installation media to access advanced recovery options, such as System Restore, Startup Repair, and Command Prompt.
- Perform a Clean Install: If all else fails, you can perform a clean install of Windows 10, which will erase your hard drive and install a fresh copy of the operating system.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Windows 10 Boot Failures
1. What are the most common signs of a hard drive failure?
- Clicking or grinding noises: These sounds indicate mechanical issues within the hard drive.
- Slow performance: A failing hard drive can cause the system to run sluggishly and respond slowly to commands.
- Frequent crashes or freezes: A failing hard drive can cause the system to crash or freeze unexpectedly.
- Error messages: The system may display error messages related to the hard drive, such as "disk read error" or "file system error."
2. How can I check the health of my hard drive?
- Use a hard drive diagnostic tool: CrystalDiskInfo and SeaTools are popular free tools that can assess the health of your hard drive.
- Run the built-in Windows CHKDSK tool: This tool can scan for and repair errors on your hard drive.
3. What is the difference between BIOS and UEFI?
- BIOS (Basic Input/Output System): An older firmware interface that manages the system’s hardware and initiates the boot process.
- UEFI (Unified Extensible Firmware Interface): A newer firmware interface that offers improved features, such as faster boot times, enhanced security, and support for larger hard drives.
4. How can I access the BIOS/UEFI setup menu?
- Press a specific key during startup: The key to access the BIOS/UEFI setup menu varies depending on the manufacturer. Common keys include F2, F10, Del, or Esc.
- Refer to your motherboard manual: The manual for your motherboard will provide instructions on how to access the BIOS/UEFI setup menu.
5. How can I create a Windows 10 installation media?
- Use the Media Creation Tool: Microsoft provides a free tool called the Media Creation Tool that allows you to create a bootable USB drive or DVD containing the Windows 10 installation files.
6. What is a clean install of Windows 10?
- A clean install erases your hard drive and installs a fresh copy of Windows 10. This process can resolve various software issues and restore your system to a pristine state.
Tips for Preventing Windows 10 Boot Failures:
- Regularly back up your data: Create regular backups of your important files to protect against data loss in case of a hard drive failure or other system issues.
- Keep your system updated: Install the latest Windows updates and driver updates to ensure your system is running smoothly and to fix any known security vulnerabilities.
- Run regular malware scans: Use a reputable antivirus program to scan your system for malware infections and protect your computer from malicious software.
- Monitor your system’s temperature: Ensure your computer is not overheating, as excessive heat can damage hardware components.
- Avoid power surges: Use a surge protector to protect your computer from power surges that can damage hardware components.
Conclusion:
Windows 10 boot failures can be a frustrating experience, but by understanding the underlying causes and following the troubleshooting steps outlined in this guide, you can effectively diagnose and resolve these issues. Remember to approach troubleshooting with a methodical and patient approach, and don’t hesitate to seek help from online forums, technical support websites, or a qualified technician if you encounter difficulties. By taking preventive measures and staying proactive, you can minimize the chances of encountering boot failures and ensure a smooth and efficient computing experience.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Unraveling the Mystery of Windows 10 Boot Failures: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!