Windows 10 Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your Digital Life
Related Articles: Windows 10 Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your Digital Life
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Windows 10 Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your Digital Life. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Windows 10 Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your Digital Life
In today’s digital landscape, where information flows freely and online threats are ever-present, robust security measures are paramount. Windows 10, Microsoft’s flagship operating system, recognizes this critical need and incorporates an extensive arsenal of security features designed to protect users from the ever-evolving world of malware. This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted security framework embedded within Windows 10, providing a thorough understanding of its capabilities and how users can maximize their digital safety.
Understanding the Threat: The Ever-Evolving Malware Landscape
Malware, short for malicious software, encompasses a wide range of digital threats designed to infiltrate and disrupt computer systems. These malicious programs can steal sensitive data, compromise privacy, disable systems, or even hold them hostage for ransom. The threat landscape is constantly evolving, with new malware variants emerging frequently, making it crucial to stay informed and adapt defensive strategies accordingly.
Windows 10: A Fortress Against Digital Threats
Windows 10 boasts a layered security approach, integrating multiple defense mechanisms to combat malware at various stages. These measures work in tandem to provide comprehensive protection, ensuring a secure and reliable computing experience.
1. Windows Defender: The First Line of Defense
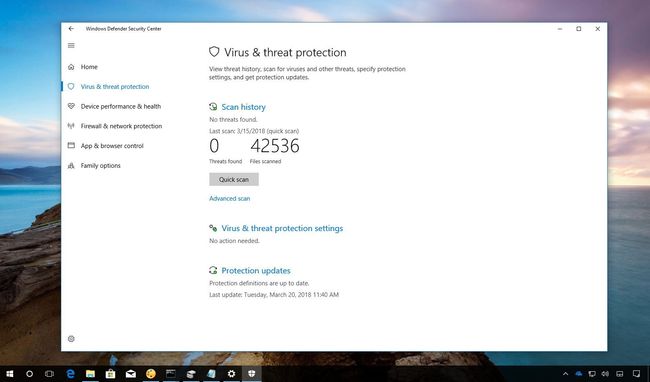
Windows Defender, Microsoft’s built-in antivirus software, acts as the first line of defense against malware. It proactively scans for and removes known threats, constantly updating its malware signature database to stay ahead of emerging threats.
- Real-Time Protection: Windows Defender monitors system activity in real-time, identifying and blocking suspicious files and applications before they can cause harm.
- On-Demand Scans: Users can initiate manual scans to thoroughly check their system for any potential malware infections.
- Automatic Updates: Windows Defender automatically updates its virus definitions and security features, ensuring continuous protection against the latest threats.
2. Windows Security: A Comprehensive Security Hub
Windows Security, previously known as Windows Defender Security Center, serves as a central hub for managing various security features within Windows 10. It provides users with a unified interface to control and monitor various security settings, including:
- Firewall: The built-in firewall controls incoming and outgoing network traffic, blocking unauthorized connections and preventing malware from entering the system.
- App & Browser Control: This feature allows users to define specific rules for app and browser behavior, restricting access to potentially harmful websites and applications.
- Device Security: Windows Security monitors the overall security posture of the device, identifying vulnerabilities and providing guidance on improving security settings.
3. SmartScreen: Filtering Out Suspicious Content
SmartScreen, a built-in feature, acts as a proactive filter against malicious websites and downloads. It analyzes website reputation and file characteristics to identify potential threats, preventing users from accessing harmful content or downloading malicious files.
- Website Filtering: SmartScreen warns users about potentially unsafe websites, preventing access to phishing or malware-infected sites.
- File Download Protection: When downloading files from the internet, SmartScreen analyzes their reputation and warns users if a file is deemed suspicious.
4. Windows Update: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Regularly updating Windows 10 is crucial for maintaining its security posture. Updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities and improve existing security features, ensuring the system remains protected against emerging threats.
- Automatic Updates: By enabling automatic updates, users ensure their system is always running the latest security patches, minimizing the risk of vulnerabilities.
- Manual Updates: Users can manually check for and install updates, ensuring their system is up-to-date.
5. User Account Control (UAC): A Barrier Against Unauthorized Changes
UAC prompts users for permission before making significant system changes or installing software, preventing malware from silently taking control of the system.
- Elevated Privileges: UAC requires users to provide administrator privileges for actions that could potentially impact system stability or security.
- Reduced Risk: By requiring user consent for significant changes, UAC minimizes the risk of malware exploiting system vulnerabilities.
6. Microsoft Defender Antivirus: Enhanced Protection for Businesses
Microsoft Defender Antivirus, a cloud-based security solution, offers advanced protection for businesses and enterprise users. It provides comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities, including:
- Next-Generation Antivirus: Defender Antivirus utilizes advanced machine learning and artificial intelligence to identify and neutralize sophisticated malware threats.
- Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Defender Antivirus provides real-time threat monitoring and response capabilities, enabling swift action against active malware threats.
Beyond the Basics: Enhancing Windows 10 Security
While Windows 10 offers a robust security framework, users can further enhance their protection by implementing additional measures:
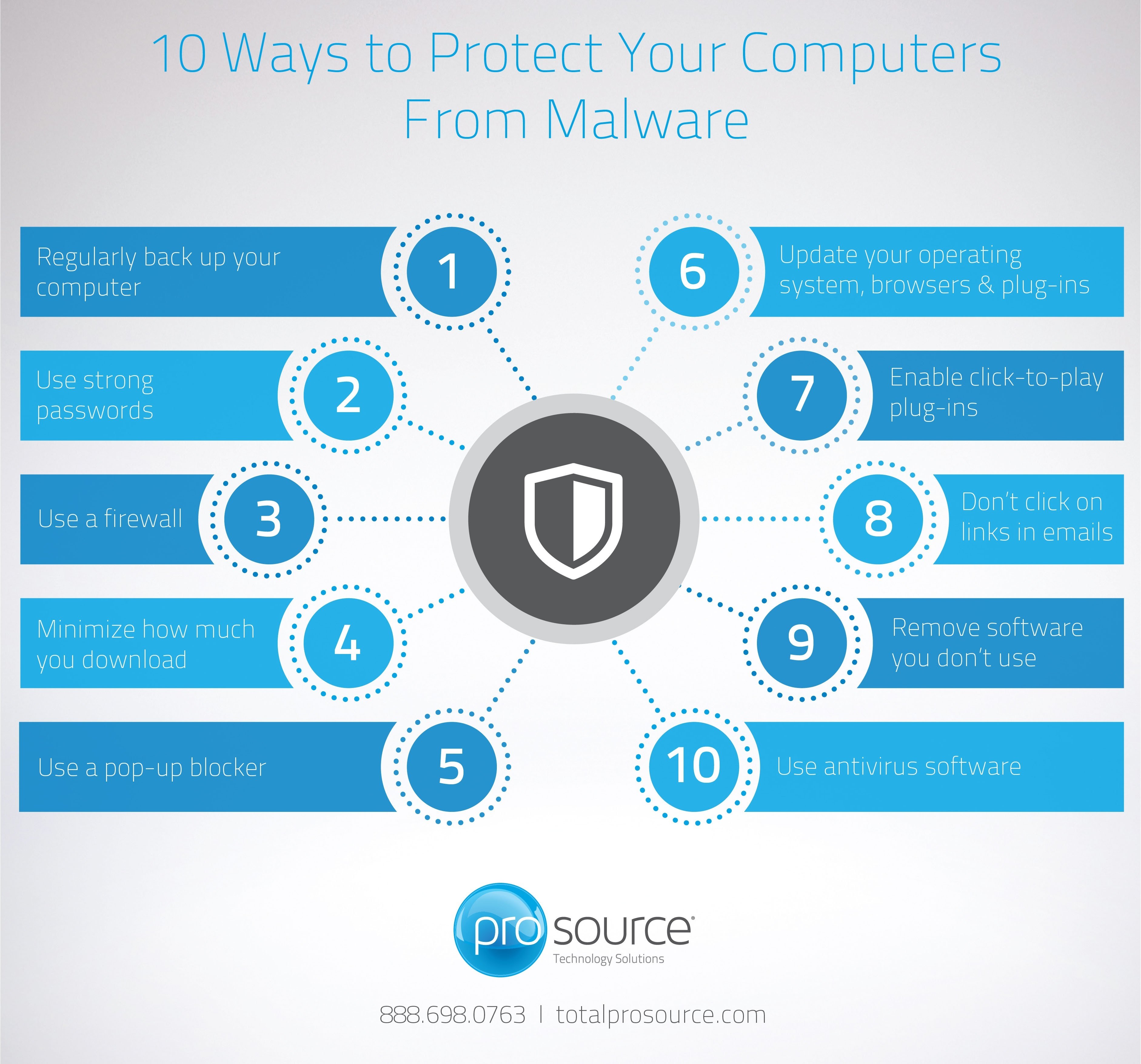
- Strong Passwords: Using strong, unique passwords for each account is crucial for preventing unauthorized access.
- Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Enabling 2FA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to enter a unique code in addition to their password.
- Regular Backups: Creating regular backups of important data safeguards against data loss in the event of a malware attack.
- Anti-Phishing Awareness: Educating oneself about phishing scams and recognizing suspicious emails or websites helps prevent falling victim to these attacks.
- Software Updates: Keeping all software up-to-date is crucial, as updates often address security vulnerabilities.
- Use of a VPN: A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts internet traffic, making it harder for malicious actors to intercept sensitive data.
FAQs on Windows 10 Malware Protection
1. What are the most common types of malware targeting Windows 10 users?
Common malware types include:
- Viruses: These programs replicate themselves and spread to other systems, often causing damage to files and system performance.
- Worms: Similar to viruses, worms spread through networks, exploiting vulnerabilities to infect other devices.
- Trojan Horses: These programs disguise themselves as legitimate software, but once installed, they can steal data, compromise the system, or allow attackers to gain control.
- Ransomware: This type of malware encrypts user files and demands payment for their decryption.
- Spyware: This malware secretly monitors user activity, collecting sensitive information such as browsing history, keystrokes, and login credentials.
2. How do I know if my Windows 10 computer is infected with malware?
Signs of malware infection include:
- Slow system performance: Malware can consume system resources, leading to slowdowns and crashes.
- Unexpected pop-ups and advertisements: Malware can hijack web browsers and display unwanted advertisements.
- Missing or corrupted files: Malware can delete or corrupt files, leading to data loss or system errors.
- Unusual network activity: Malware can communicate with remote servers, increasing network usage and slowing down internet connection.
- Suspicious processes running in the background: Malware can install hidden processes that run in the background, consuming system resources and potentially stealing data.
3. How can I remove malware from my Windows 10 computer?
If you suspect your computer is infected with malware, take the following steps:
- Run a full system scan with Windows Defender: This can help identify and remove known malware threats.
- Consider using a specialized malware removal tool: There are several reputable malware removal tools available that can help detect and remove even the most sophisticated threats.
- Reset your computer to factory settings: This is a last resort option, but it can help remove persistent malware infections.
4. Can I use third-party antivirus software alongside Windows Defender?
While Windows Defender provides a robust level of protection, using a third-party antivirus software can offer additional layers of security, particularly for users who handle sensitive data or frequently visit risky websites. However, it’s crucial to choose reputable antivirus software and ensure compatibility with Windows 10.
5. How often should I update Windows 10 to ensure optimal security?
Microsoft releases security updates regularly, addressing vulnerabilities and improving existing security features. To ensure optimal security, it’s recommended to install updates as soon as they become available. Enable automatic updates to ensure your system is always running the latest security patches.
Tips for Maintaining Windows 10 Security
- Practice safe browsing habits: Avoid clicking on suspicious links, downloading files from untrusted sources, and opening attachments from unknown senders.
- Use strong passwords and enable two-factor authentication: Strong passwords and 2FA provide an extra layer of protection against unauthorized access.
- Be wary of phishing scams: Phishing emails and websites try to trick users into revealing sensitive information. Be cautious of suspicious emails and websites, and never share personal information with unfamiliar sources.
- Keep your software up-to-date: Software updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities.
- Use a reputable antivirus software: A good antivirus program can detect and remove malware threats, providing an additional layer of protection.
- Be cautious when using public Wi-Fi networks: Public Wi-Fi networks are often less secure than private networks, making it easier for attackers to intercept data. Use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi networks to encrypt your traffic.
- Regularly back up your data: Backups can help you recover data in the event of a malware attack or system failure.
Conclusion
Windows 10 offers a comprehensive security framework designed to protect users from a wide range of malware threats. By understanding the security features built into the operating system and implementing best practices, users can significantly reduce their risk of encountering malware and safeguard their digital lives. Continuous vigilance and proactive measures are essential in the ever-evolving world of cyber threats. Staying informed, updating software regularly, and practicing safe browsing habits are key to maintaining a secure and reliable computing experience.







Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Windows 10 Malware Protection: A Comprehensive Guide to Safeguarding Your Digital Life. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!